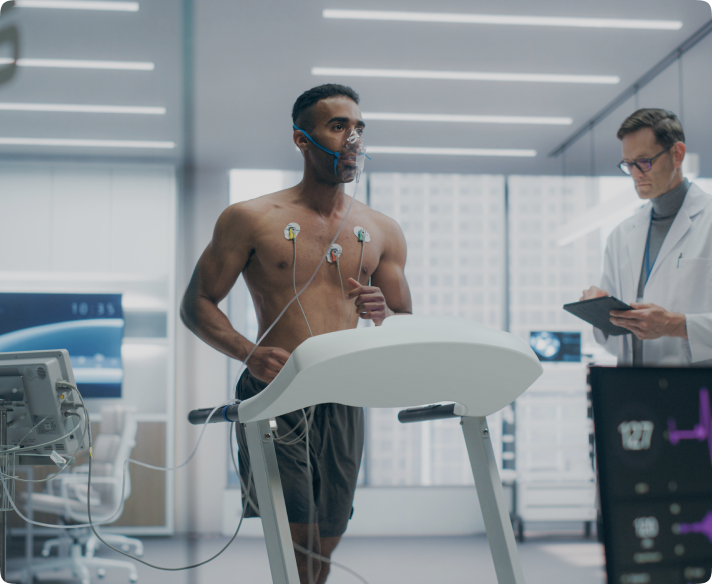
When you visit a cardiologist for symptoms like chest pain, breathlessness, or palpitations, one of the first tools we may use is an exercise stress test. Also known as an “exercise ECG” or “treadmill test,” it helps us understand how your heart responds to physical activity. While the test itself is simple, the information it gives us is incredibly valuable.
A stress test monitors your heart’s rhythm, electrical activity, and blood pressure as your body works harder. This allows us to see if there’s any evidence of reduced blood flow to your heart muscle—something that might not be obvious while you’re at rest. We can also evaluate whether your symptoms are likely related to your heart, how well your medications are working, or if it’s safe for you to begin a new fitness program.
Most commonly, the test involves walking on a treadmill while connected to an ECG machine. The speed and incline increase every few minutes to gently raise your heart rate, similar to climbing stairs. If you’re unable to walk due to joint pain or mobility issues, we can use medications that mimic the effects of exercise on the heart. You’ll be monitored the entire time by trained medical staff in a controlled environment.
Stress tests are especially useful in diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD), but they’re also used to assess arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), investigate unexplained symptoms like dizziness, or evaluate the effectiveness of treatments like stents or medications. It’s one of the best non-invasive ways to “stress” your heart safely and get clear diagnostic clues.
If your results are normal, it may mean your heart is handling exercise well and there’s no sign of significant narrowing in your coronary arteries. Abnormal results may lead to further testing, such as a stress echocardiogram or a CT coronary angiogram. But even if you can’t complete the full test, the data we gather is still clinically useful.
What Happens During the Test?
- Setup: ECG leads are placed on your chest, and a cuff monitors your blood pressure.
- Exercise: You walk on a treadmill, gradually increasing speed and incline every few minutes.
- Monitoring: We track your heart rhythm, rate, blood pressure, and any symptoms.
- Cool Down: You’ll continue to be monitored as your heart rate returns to normal.
The test usually takes 30–45 minutes from start to finish.
Common Misconceptions
- “I have to be fit to do the test.”
No. The goal is to push your heart safely—not meet a fitness benchmark. - “If I don’t finish the test, it’s a failure.”
Not true. Valuable results can still be gathered even if you stop early. - “It sounds dangerous.”
It’s very safe and always done under close medical supervision.
FAQs
Q: Can I eat or drink before a stress test?
A: Please avoid caffeine for at least 24 hours before your appointment, and don’t eat a heavy meal within 2–4 hours. Water is fine.
Q: What should I wear?
A: Comfortable, loose-fitting clothing and supportive walking shoes. Avoid wearing dresses, tight tops, or stockings that can interfere with ECG placement.
Q: Will I get results straight away?
A: In many cases, yes—especially if your cardiologist is present. Sometimes the ECG data is reviewed in more detail and you’ll receive a follow-up call or letter.
Q: Is it covered by Medicare?
A: Yes, Medicare covers standard stress testing when medically indicated.
Key Takeaways
- A stress test helps determine if your heart receives enough blood when working hard
- It is safe, non-invasive, and typically takes under an hour
- The test is highly useful for diagnosing coronary artery disease and arrhythmias
- It can help guide treatment, medication changes, or the need for further testing
- Even partial test results can be very helpful to your cardiologist
Ready for a heart check-up?
If you’re experiencing symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, or palpitations—or simply want to assess your heart health — request an appointment with Apollo Cardiology, today. Early diagnosis is one of the best ways to prevent serious heart disease.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this blog is for general educational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. Do not disregard medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.